
Pre-Engineered Buildings vs. Prefabricated Structures: A Structural and Cost Analysis
In the evolving world of construction, choosing the right building method can make or break a project. Two modern approaches, Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs) vs Prefabricated Structures, have gained significant traction for their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability.
While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they represent distinct construction methodologies with unique advantages and applications.
This blog provides a comprehensive comparison of Pre-Engineered Buildings vs Prefabricated Structures, diving into their structural characteristics, cost implications, and practical benefits, supported by recent research and data.
Understanding Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs)
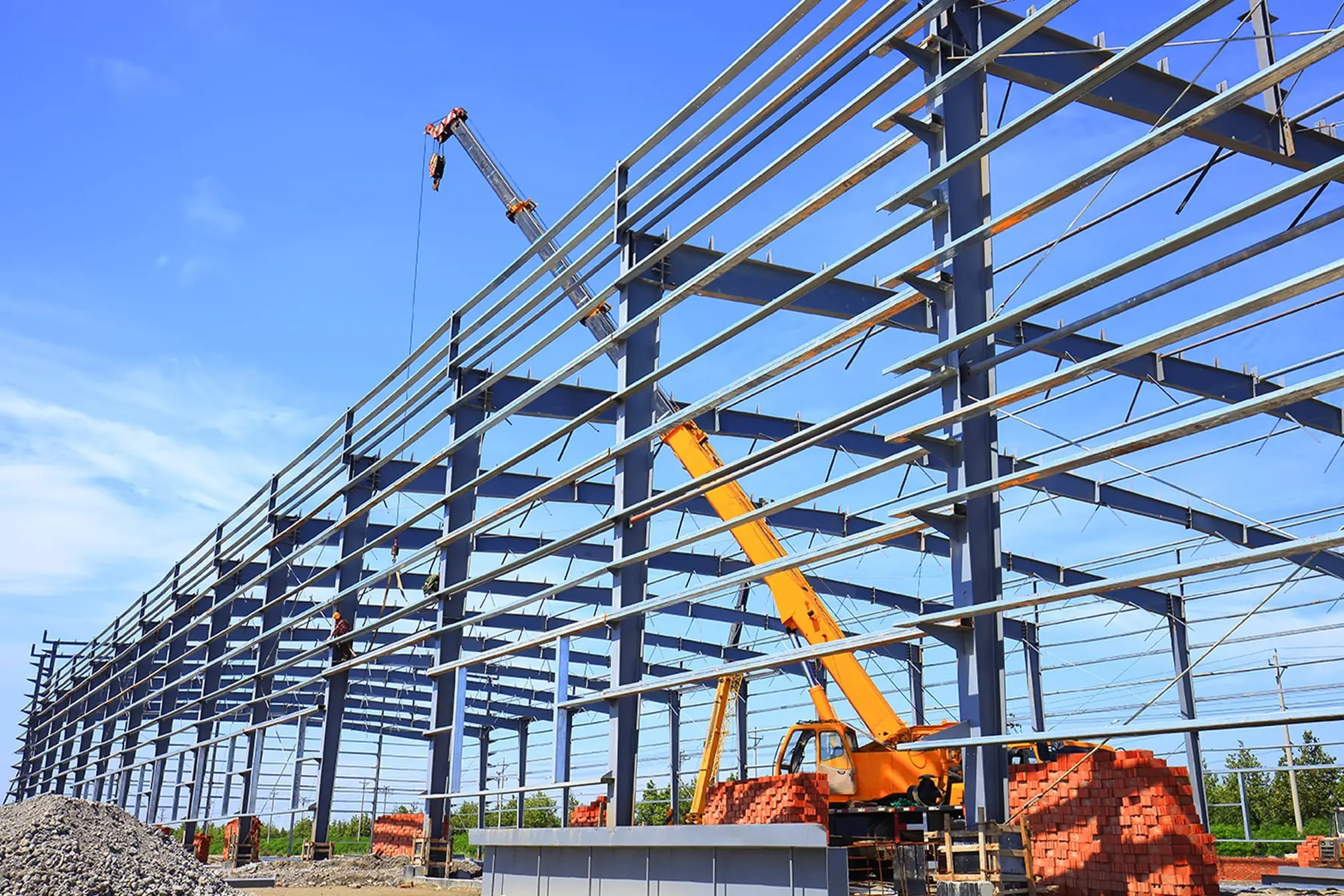
Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs) are steel structures designed and fabricated in a factory to meet specific load requirements and building codes before being shipped to the construction site for assembly.
PEBs utilize advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software to create precise structural components, such as I-beams, columns, rafters, and purlins, which are bolted together on-site. This approach minimizes on-site fabrication, reducing construction time and waste.
Key Features of PEBs
- Design Precision: PEBs are engineered using CAD and 3D modeling to optimize material use and structural integrity.
- Material: Primarily steel, with components like galvanized or stainless steel for enhanced durability.
- Applications: Widely used for industrial warehouses, commercial complexes, agricultural buildings, and aircraft hangars.
- Construction Time: Assembly typically takes 6–8 weeks due to pre-fabricated components.
Understanding Prefabricated Structures
Prefabricated Structures, often referred to as “prefab,” encompass a broader category where building components, made from materials like steel, concrete, wood, or composites—are manufactured off-site and assembled at the construction site.
Unlike PEBs, which are a subset of prefabricated buildings, prefab structures may include precast concrete panels, modular units, or light-gauge steel frames, offering flexibility in material choice and design.
Key Features of Prefabricated Structures
- Material Versatility: Can use steel, concrete, wood, or tensioned fabric for cladding and structural elements.
- Construction Process: Components are produced in a controlled factory environment, ensuring quality and reducing weather-related delays.
- Applications: Suitable for residential homes, schools, offices, and temporary structures like portable toilets.
- Customization: Offers moderate design flexibility, though not as precise as PEBs for complex load requirements.
Structural Analysis: PEBs Vs Prefabricated Structures
Structural Integrity
- PEBs: PEBs are designed for specific load conditions, including wind uplift, seismic forces, and live loads, using advanced software to ensure structural efficiency. Their steel framework, often composed of I-beams and tapered members, provides a high strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for earthquake-prone regions like Nepal. Research by Dumaru, Rodrigues, and Varum (2019) found PEBs to be more resilient under seismic loads compared to conventional steel buildings due to their optimized design.
- Prefabricated Structures: Prefab structures vary widely in structural performance depending on the material. Precast concrete prefab buildings offer excellent fire resistance and durability, while steel-based prefabs provide flexibility and seismic resilience. However, light-gauge steel or wood-based prefabs may require additional reinforcement for high-load applications. A 2023 study by Qian et al. highlighted the energy dissipation capacity of prefabricated concrete frame joints, indicating robust performance in seismic zones when enhanced with shape memory alloy bars.
Design and Flexibility
- PEBs: PEBs excel in design precision, allowing customization for large clear spans and specific aesthetic requirements, such as fascias or canopies. However, modifications after initial design can be costly due to their pre-engineered nature.
- Prefabricated Structures: Prefab buildings offer greater material flexibility but may lack the precision of PEBs for complex structural demands. They are ideal for projects requiring diverse cladding options or modular designs, such as prefabricated schools or residential units.
Table 1: Structural Comparison
| Aspect | Pre-Engineered Buildings | Prefabricated Structures |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Material | Steel (I-beams, columns, purlins) | Steel, concrete, wood, or composites |
| Design Method | CAD-based, highly precise | Varies, less precise for complex loads |
| Seismic Performance | High (optimized for seismic zones) | Varies (concrete: high; wood/light steel: moderate) |
| Customization | High within design phase, costly post-design | Moderate, flexible material choices |
| Construction Time | 6–8 weeks | 4–12 weeks, depending on material |
Cost Analysis: PEBs vs. Prefabricated Structures
Initial Costs
- PEBs: Material costs for Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs) range from 1,340–3,350 NPR per square foot. Total costs for a 10,000 sq. ft. structure range from 16,080,000–33,500,000 NPR, depending on customization. The prefabrication process reduces labor costs by up to 50% compared to traditional construction, as components are assembled quickly with minimal on-site work. A 2020 study from IOP Conference Series noted that PEBs can save up to 30% on labor and material costs due to minimal waste.
- Prefabricated Structures: Costs vary widely by material. Steel prefabs align closely with PEB costs (1,340–3,350 NPR/sq. ft.), while precast concrete structures may cost 33,500–67,000 NPR/m² more than traditional construction. Wood-based prefabs average 4,824 NPR/sq. ft., higher than steel PEBs. However, government incentives in some regions can offset prefab costs by approximately 40,200 NPR/m².
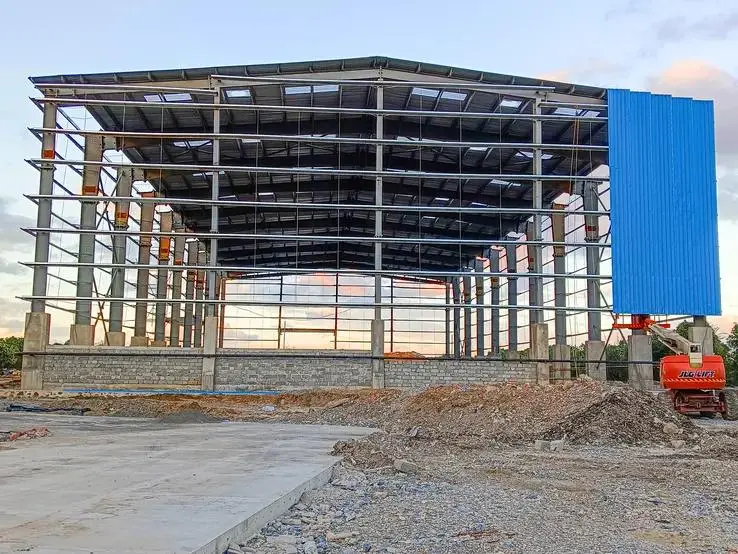

Long-Term Costs
- PEBs: PEBs offer low maintenance due to steel’s durability and resistance to rust and corrosion when properly treated. Energy-efficient insulation, such as insulated metal panels, can save 268,000–670,000 NPR on annual energy bills for a commercial setup. However, condensation issues may arise if insulation is inadequate, potentially increasing maintenance costs.
- Prefabricated Structures: Concrete prefabs have high durability and fire resistance, reducing long-term maintenance. However, wood or light-gauge steel prefabs may face issues like corrosion or pest damage, increasing upkeep costs. Energy efficiency varies, with concrete prefabs lagging behind steel in thermal performance.
Table 2: Cost Comparison
| Cost Factor | Pre-Engineered Buildings | Prefabricated Structures |
|---|---|---|
| Material Cost | 1,340–3,350 per sq.ft NPR (steel) | 1,340–3,350 NPR per sq.ft (steel, concrete, wood) |
| Labor Cost | Low (50% less than traditional) | Varies (low for steel, high for concrete) |
| Construction Time | 6–8 weeks, lower labor costs | 4–12 weeks, varies by material |
| Maintenance | Low (steel durability) | Varies (low for concrete, higher for wood) |
| Energy Savings | 10–20% annually | 5–15% annually, depending on material |
Advantages and Disadvantages
Pre-Engineered Buildings
- Advantages:
- Speed: Rapid assembly (6–8 weeks) due to pre-fabricated components.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Minimal waste and optimized material use reduce costs.
- Seismic Resilience: High strength-to-weight ratio suits earthquake-prone areas.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited Modifications: Post-design changes are costly and complex.
- Condensation Risks: Poor insulation can lead to moisture issues.
Prefabricated Structures
- Advantages:
- Material Flexibility: Options like concrete or wood suit diverse aesthetic and functional needs.
- Environmental Benefits: Controlled factory production reduces site disruption and waste.
- Disadvantages:
- Variable Costs: Concrete prefabs can be pricier than steel PEBs.
- Structural Limitations: Light-gauge steel or wood may not support heavy loads without reinforcement.
Applications and Suitability
- PEBs: Ideal for industrial and commercial projects requiring large clear spans, such as warehouses, factories, or sports facilities. Their seismic resilience makes them a top choice in regions like Nepal, where HIPCO Superbuild PEB is pioneering their use.
- Prefabricated Structures: Suited for residential, educational, and temporary structures. Precast concrete prefabs are popular for high-rise buildings, while modular prefabs serve rural schools or affordable housing.
Recent Research Insights
- A 2023 study by Wu et al. analyzed the seismic performance of prefabricated subway station structures, finding that steel-based prefabs outperform concrete in flexibility but require careful joint design.
- A 2020 IOP Conference Series report highlighted that prefabricated construction can save 27.33% in construction time compared to traditional methods, with steel PEBs leading in cost savings.
- Research by Dumaru et al. (2019) emphasized PEBs’ cost-benefit advantages in seismic zones, with up to 30% weight reduction compared to conventional steel buildings.
Choosing the Right Option: Pre-Engineered Buildings Vs Prefabricated
The choice between Pre-Engineered Buildings vs Prefabricated Structures depends on project requirements:
- Choose PEBs for projects prioritizing speed, seismic resilience, and cost-efficiency in industrial or commercial settings.
- Choose Prefabricated Structures for flexibility in materials, residential applications, or projects with unique aesthetic demands.
Conclusion
Both Pre-Engineered Buildings and Prefabricated Structures offer innovative solutions to modern construction challenges, balancing speed, cost, and structural integrity.
PEBs excel in precision, seismic performance, and cost-effectiveness for industrial applications, while prefabricated structures provide material versatility and environmental benefits for diverse projects.
By understanding their structural and cost differences, supported by recent research, you can make an informed decision tailored to your project’s needs.
Whether it’s a warehouse in Nepal or a modular school in India, the right choice will elevate your construction experience.
For further inquiries or project consultations, contact industry leaders like HIPCO Superbuild PEB or explore resources from Viking Steel Structures for tailored solutions.
Read more: PEB Structure Vs. Traditional Construction: Which is Better for Nepal?



