
PEB Structures Vs Traditional Construction: Which Is Better for Nepal?
Nepal’s construction sector is at a crossroads, balancing modern innovation with time-tested methods. The debate of PEB vs traditional construction is central to this evolution, especially for industrial and commercial projects.
Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs) offer a modern, factory-fabricated approach, while traditional construction relies on conventional, on-site methods.
To help businesses and developers make informed decisions, this article compares PEB vs traditional construction across critical factors, tailored to Nepal’s unique needs.
1. Speed of Construction: Time is Money
Time is a critical factor in Nepal’s growing economy, where businesses need quick turnaround times to stay competitive. The PEB vs traditional construction debate highlights stark differences in construction speed.
PEB Structures
PEBs are manufactured in controlled factory environments and assembled on-site. This streamlined process drastically cuts construction time. For example, a medium-sized warehouse that typically takes six months with traditional methods can be completed in just 8-12 weeks using PEBs. The pre-fabrication process minimizes delays, as components are ready to assemble upon delivery.
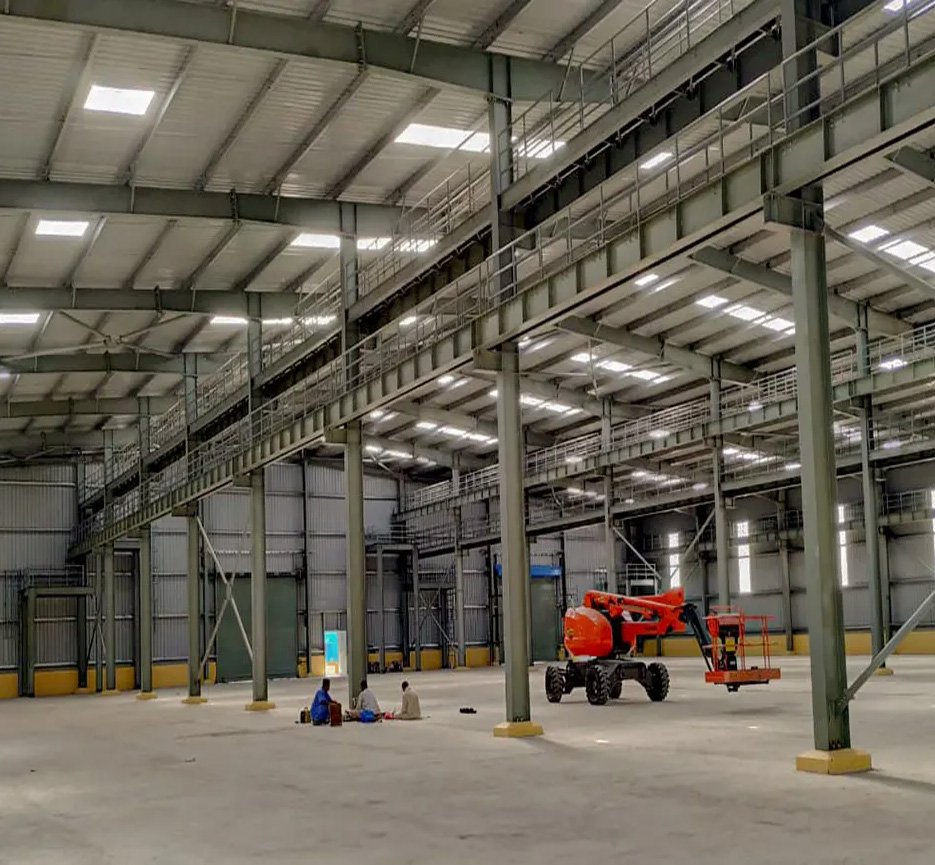

Traditional Construction
Traditional construction involves labor-intensive tasks like bricklaying, concrete pouring, and curing. These processes are time-consuming and often face delays due to weather conditions, labor shortages, or material availability. In Nepal’s monsoon-heavy climate, these delays can extend project timelines significantly.
| Aspect | PEB Structures | Traditional Construction |
| Construction Time | 8-12 weeks for a warehouse | 6-8 months for a warehouse |
| Weather Dependency | Minimal, as most work is off-site | High, due to on-suite curing and masonry |
| Labor Requirement | Lower, assembly-focused | Higher, labor-intensive processes |
Verdict: In the PEB vs traditional construction comparison, PEBs are the clear winner for speed, making them ideal for time-sensitive industrial projects in Nepal.
2. Cost Efficiency: Budget-Friendly Solutions
Cost is a major consideration in Nepal, where budgets for industrial and commercial projects are often constrained. The PEB vs traditional construction debate reveals significant cost differences.
PEB Structures
PEBs are designed to minimize costs through efficient use of materials and labor. Factory fabrication reduces waste, and standardized components lower production costs. On-site assembly requires fewer workers, further cutting expenses. For large-scale projects, PEBs can save up to 20-30% compared to traditional methods.
Traditional Construction
Traditional methods often lead to higher costs due to prolonged timelines, material wastage, and labor expenses. For instance, concrete and brick construction requires extensive raw materials, which can be costly in Nepal due to transportation challenges. Unexpected delays also add to labor and equipment costs.
Comparison Table: Cost Efficiency
| Aspect | PEB Structures | Traditional Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Material Wastage | Minimal, precise fabrication | High, due to on-site cutting and errors |
| Labor Costs | Lower, fewer workers needed | Higher, labor-intensive processes |
| Overall Cost | 20-30% cheaper for large projects | Higher due to extended timelines |
Verdict: For cost-conscious developers, PEBs offer a budget-friendly solution in the PEB vs traditional construction comparison, especially for industrial and commercial projects.
Read more: PEB Cost in Nepal: How Pre-Engineered Buildings Save Money in Construction
3. Durability and Safety: Built to Last
Nepal’s location in a seismically active zone makes durability and safety critical in construction. The PEB vs traditional construction debate underscores how each method addresses these concerns.
PEB Structures
PEBs are engineered with precision, using high-quality steel that meets international standards. Their lightweight yet strong design makes them highly earthquake-resistant, a vital feature for Nepal. PEBs are also built to withstand extreme weather, including heavy monsoon rains and strong winds, ensuring long-term durability.
Traditional Construction
Traditional buildings, often made of concrete and bricks, can be durable but require specific reinforcements to meet seismic standards. Without proper engineering, these structures may be vulnerable to earthquakes, posing safety risks. Retrofitting for seismic resistance can also increase costs.
Comparison Table: Durability and Safety
| Aspect | PEB Structures | Traditional Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Earthquake Resistance | High, lightweight steel design | Moderate, requires reinforcement |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent, corrosion-resistant | Good, but prone to water damage |
| Lifespan | 30-50 years with minimal maintenance | 20-40 years, depending on maintenance |
Verdict: In the PEB vs traditional construction comparison, PEBs provide superior durability and safety, making them a safer choice for Nepal’s seismic and climatic challenges.
4. Sustainability: A Greener Alternative
Sustainability is a growing priority in Nepal, aligning with global goals like the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The PEB vs traditional construction debate highlights their environmental impact.
PEB Structures
PEBs are eco-friendly due to:
- Recyclable Materials: Steel used in PEBs is recyclable, reducing resource depletion.
- Minimal Waste: Factory fabrication ensures precise material use, minimizing waste.
- Energy Efficiency: PEBs consume less energy during construction and can incorporate energy-saving features like insulation.
These factors make PEBs a sustainable choice for Nepal’s green building initiatives.
Traditional Construction
Traditional methods rely heavily on concrete and bricks, which have a high environmental footprint. Cement production contributes to carbon emissions, and on-site construction generates significant waste. These factors make traditional construction less sustainable.
Comparison Table: Sustainability
| Aspect | PEB Structures | Traditional Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Material Usage | Recyclable steel, minimal waste | High-use concrete, non-recyclable |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower, energy-efficient processes | Higher, due to cement production |
| Waste Generation | Minimal, factory-controlled | High, due to on-site processes |
Verdict: PEBs are the greener choice in the PEB vs traditional construction comparison, supporting Nepal’s sustainability goals.
5. Flexibility and Adaptability: Meeting Future Needs
Nepal’s industries are growing, requiring buildings that can adapt to changing needs. The PEB vs traditional construction debate highlights flexibility as a key differentiator.
PEB Structures
PEBs are modular, allowing easy expansion or modification. Businesses can add new sections or reconfigure layouts without significant costs. This adaptability is ideal for industries like manufacturing or warehousing, which may need to scale operations.
Traditional Construction
Traditional buildings are rigid, making modifications costly and time-consuming. Expanding a concrete structure often requires demolishing and rebuilding parts, which can disrupt operations.
Comparison Table: Flexibility
| Aspect | PEB Structures | Traditional Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Expansion Ease | Easy, modular design | Difficult, requires major reconstruction |
| Modification Cost | Low, bolt-on additions | High, structural changes needed |
| Scalability | High, adaptable to growth | Limited, rigid design |
Verdict: PEBs excel in flexibility, making them the better choice in the PEB vs traditional construction comparison for Nepal’s dynamic industries.
6. Aesthetic and Functional Design
Modern projects in Nepal demand both functionality and aesthetics. The PEB vs traditional construction debate explores how each method delivers on design.
PEB Structures
PEBs use advanced design software to create functional yet visually appealing structures. They offer customizable facades, roofing, and layouts, making them suitable for warehouses, factories, or commercial spaces. Their sleek, modern look aligns with Nepal’s evolving urban landscape.
Traditional Construction
Traditional methods allow for intricate designs, especially in residential projects. However, for industrial applications, they may lack the streamlined efficiency of PEBs. Achieving modern aesthetics can also increase costs.
Comparison Table: Design
| Aspect | PEB Structures | Traditional Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Aesthetic Options | Modern, customizable designs | Highly customizable, but costly |
| Functional Efficiency | High, optimized for industrial use | Moderate, better for residential use |
| Design Speed | Fast, software-driven | Slower, manual design processes |
Verdict: PEBs offer a balanced approach to aesthetics and functionality in the PEB vs traditional construction comparison, ideal for Nepal’s commercial needs.
Conclusion
The PEB vs traditional construction debate reveals that PEBs are the superior choice for Nepal’s industrial and commercial projects. Their speed, cost-efficiency, durability, sustainability, flexibility, and modern design make them ideal for a country navigating seismic risks, budget constraints, and sustainability goals.
While traditional construction remains relevant for smaller, residential projects, PEBs address the demands of Nepal’s growing industries.
Ready to explore PEB solutions for your next project? Contact PEB Nepal today for tailored, cost-efficient, and eco-friendly building solutions.
Recommended reading: Top 5 Benefits of Using PEB Structures for Industrial Projects in Nepal



